Frameworks of Marketing Strategies: Building a Structured, Tailored Approach for Success
-rident.webp)
Frameworks of Marketing Strategies: Building a Structured, Tailored Approach for Success
In the complex and dynamic marketing world, strategies can’t just be created on the fly; they need a structured approach that aligns with business goals, market demands, and customer needs. This is where marketing frameworks come into play. These frameworks provide a blueprint for developing, executing, and refining marketing strategies. Versatile and adaptable, these frameworks can be tailored to fit specific marketing objectives and scenarios, empowering businesses to achieve consistent results and adapt as needs change.
Here, we’ll explore some popular marketing frameworks, highlighting their versatility and how they can help marketers navigate challenges and drive growth.
Why Use Marketing Frameworks?
Before diving into specific frameworks, understanding the “why.” Marketing frameworks:
• Provide Structure: They help break down complex strategies into manageable parts, making it easier to plan and execute.
• Promote Consistency: Using a framework keeps teams on the same page, ensuring a cohesive approach across departments.
• Enhance Flexibility: Frameworks can be adjusted to fit different objectives, customer segments, or product lines, making them ideal for businesses of all sizes.
• Enable Measurement: With clear steps and metrics, frameworks make it easy to track progress and measure the impact of your strategies.
Considering these benefits, let’s explore some of the most widely used marketing frameworks and their applications.
1. SOSTAC: A Comprehensive Planning Tool
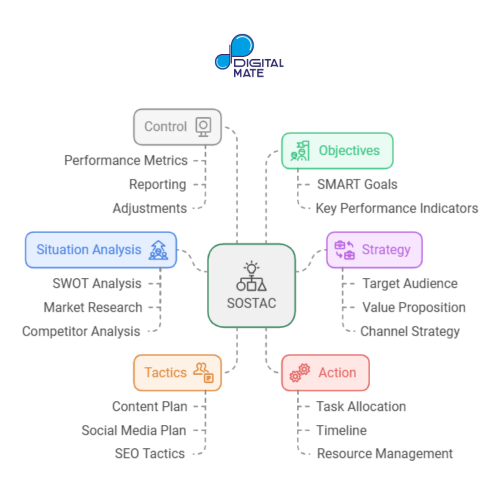
SOSTAC stands for Situation Analysis, Objectives, Strategy, Tactics, Action, and Control. This framework provides a structured approach to planning, from understanding the current market situation to executing and controlling the strategy.
• Situation Analysis helps assess the brand's current status through tools like SWOT analysis.
• Objectives set clear, measurable goals, often structured around SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound) principles.
• Strategy defines the broad approach to achieve these goals, such as targeting specific customer segments.
• Tactics detail the specific tools, campaigns, and activities that support the strategy.
• Action involves assigning roles, budgets, and timelines for implementation.
• Control provides ongoing monitoring and adjustments to optimize performance.
Versatility: SOSTAC’s step-by-step structure is adaptable, making it suitable for high-level strategic planning and more granular, campaign-level initiatives. Businesses can modify each step to fit unique objectives, from product launches to customer retention campaigns.
2. The 7 Ps Marketing Mix: The Holistic Approach
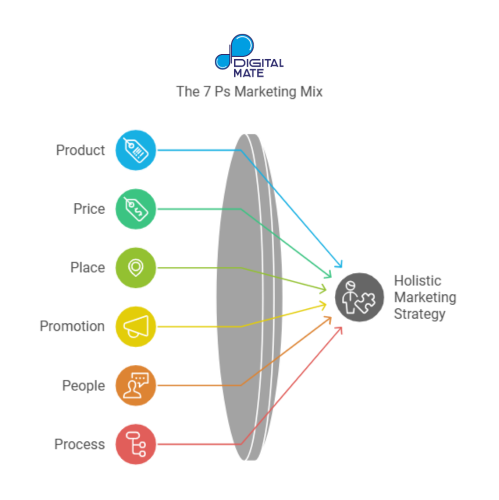
The 7 Ps Marketing Mix framework (Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence) is essential for refining a business's market positioning.
• Product: Define what the brand is offering and its unique value.
• Price: Determine pricing strategies based on market demand and competitor pricing.
• Place: Identify the distribution channels best suited to reach target customers.
• Promotion: Plan promotional activities, including ads, social media, and content.
• People: Ensure everyone involved in customer interactions represents the brand well.
• Process: To ensure a seamless customer experience, map out the delivery process.
• Physical Evidence: Create tangible elements, such as packaging, that reinforce the brand image.
Versatility: The 7 Ps can be adjusted to fit any business model, from retail to services. For example, a tech startup might focus on “Process” to ensure app users have a smooth onboarding experience. In contrast, a luxury brand might focus on “Physical Evidence” to enhance product packaging and reinforce brand prestige.
3. SWOT Analysis: The Strategic Snapshot
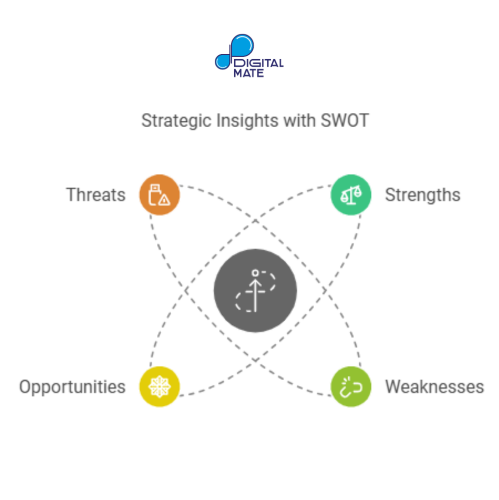
SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is a simple yet powerful framework for assessing internal and external factors that impact strategy.
• Strengths and Weaknesses examine internal aspects, such as product quality or operational efficiency.
• Opportunities and Threats focus on external factors like market trends or new competitors.
Versatility: SWOT can be applied to anything from a full brand audit to a single campaign. It’s also easy to customize; for example, an online retailer might use SWOT to assess strengths like fast shipping or weaknesses like limited payment options, tailoring the strategy to address these insights.
4. RACE Framework: Digital Marketing Excellence

The RACE framework—Reach, Act, Convert, Engage—is designed specifically for digital marketing and focuses on the customer journey from awareness to advocacy.
• Reach: Build brand awareness through various digital channels.
• Act: Engage users with valuable content that encourages interaction.
• Convert: Drive conversions, whether through sales, subscriptions, or other actions.
• Engage: Foster long-term loyalty and repeat business.
Versatility: RACE is ideal for guiding digital campaigns, but it can also be used to map out customer journeys. For example, an e-commerce site can use RACE to plan how to engage visitors, convert them into customers, and keep them returning.
5. AIDA: The Customer Engagement Model

The AIDA model—Attention, Interest, Desire, Action—focuses on guiding customers through the buying process.
• Attention: Capture the audience’s attention with eye-catching ads or headlines.
• Interest: Engage them by showcasing relevant benefits.
• Desire: Create a desire for the product by highlighting unique selling points.
• Action: Encourage customers to take the next step, such as purchasing.
Versatility: AIDA is beneficial for crafting content that guides customers through each decision-making stage. It’s flexible enough for quick social media posts and long-form sales pages, making it an adaptable tool for diverse marketing formats.
6. Customer Journey Mapping: The Path to Understanding

Customer Journey Mapping is a visual framework that details each step a customer takes when interacting with a brand.
• Awareness: How customers first hear about the brand.
• Consideration: The research phase where customers weigh their options.
• Purchase: When customers make the actual purchase.
• Retention: Post-purchase activities that keep customers engaged.
• Advocacy: Turning satisfied customers into brand advocates.
Versatility: This framework is invaluable for understanding pain points and tailoring strategies to enhance the customer experience. For example, a travel agency might use journey mapping to understand customers' needs at each stage of a trip, from planning to returning home.
7. STP: Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
The STP framework helps businesses refine who they target and how they position their product to meet audience needs.
• Segmentation: Divide the market into distinct groups with similar characteristics.
• Targeting: Choose the segments that best align with the brand’s offering.
• Positioning: Craft a message that resonates with the target audience and stands out from competitors.
Versatility: STP is adaptable across industries and marketing goals. A luxury brand, for instance, may use this framework to target high-income consumers and position itself as an exclusive option. In contrast, a mass-market brand may focus on affordability and accessibility.
Why Versatile Frameworks Are Essential in Marketing
Marketing frameworks are more than a checklist; they are adaptable tools that can evolve alongside a brand’s goals, audience, and market conditions. Here’s why this versatility is crucial:
1. Tailoring for Specific Objectives: Frameworks can be customized to address unique goals, such as brand awareness or customer retention.
2. Flexibility Across Scenarios: From launching a new product to repositioning an existing one, frameworks provide a reliable structure adaptable to different contexts.
3. Data-Driven Adjustments: Marketers can adjust frameworks to optimize for better results without starting from scratch by monitoring key metrics.
4. Streamlined Execution: Frameworks create a roadmap that aligns cross-functional teams, making strategy execution more efficient and cohesive.
Marketing frameworks like SOSTAC, 7 Ps, SWOT, RACE, and AIDA offer marketers versatile, structured approaches to strategy development and execution. By tailoring these frameworks to fit specific goals and scenarios, businesses can maximize their marketing efforts and build a foundation for long-term success. In an ever-evolving digital landscape, adaptable frameworks are not just tools; they are essential guides that bring clarity, direction, and measurable results to any marketing campaign.

.webp)





